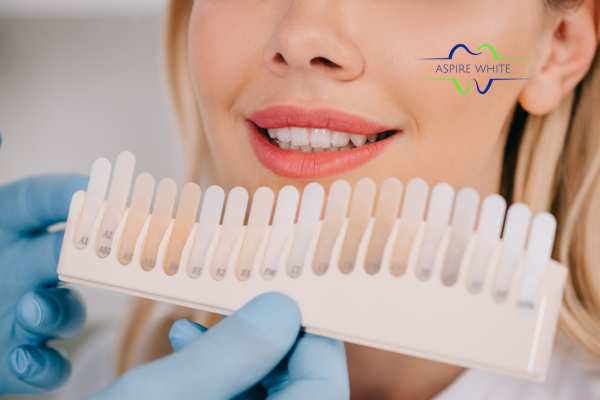
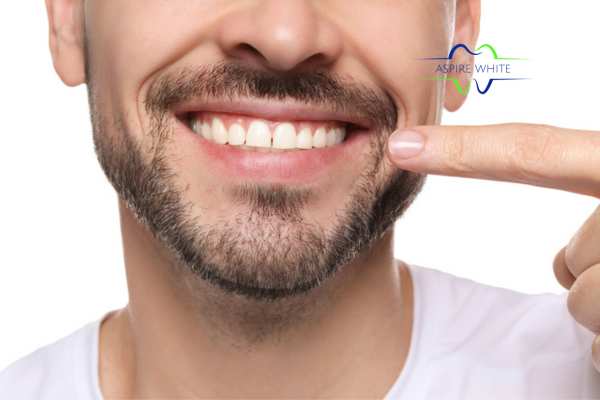
We all want our smile to be the brightest thing in the room, but sometimes our daily eating habits quietly work against us. Many people don’t realise that teeth staining isn’t just about poor brushing—it’s often a direct result of the foods and drinks we consume.
Dark pigments in coffee, tea, red wine, and certain sauces can cling to the enamel, creating a dull or yellowish hue over time. Even seemingly harmless favourites like berries or tomato-based dishes can gradually discolour teeth. See Here Is Laser Teeth Whitening the Fastest Method?
We understand this frustration all too well. Our at-home laser teeth-whitening treatment is designed to tackle these diet-related stains quickly and effectively, giving you a fresher, brighter smile without sacrificing the foods you love.
Have you ever felt self-conscious about discolouration after your morning coffee Nottingham?
For many of us, coffee is the fuel that powers our mornings—but it’s also one of the top culprits for staining teeth. Those rich, dark pigments (known as tannins) penetrate the tiny pores in your enamel, leaving a lingering yellow or brown tone.
It’s not just about appearance, either—coffee stains can make you feel less confident in professional meetings, social gatherings, or even in photos.
Aspire White’s Nottingham gentle, at-home laser whitening treatment can reverse these effects in just a few sessions, letting you keep your coffee habit without the nagging worry about your smile.
How might your favourite foods unintentionally be dulling your smile?
It’s not just the obvious culprits like wine or coffee—many everyday foods can slowly rob your teeth of their natural sparkle. Curry, balsamic vinegar, beetroot, and soy sauce are rich in pigments that can lodge in enamel.
Acidic foods, like citrus fruits or fizzy drinks, don’t stain directly but can weaken enamel, making it more susceptible to absorbing colour from other foods. Check out Laser Teeth Whitening and Receding Gums: Challenges and Considerations
At Aspire WhiteNottingham, we believe you shouldn’t have to choose between enjoying your favourite meals and having a bright, confident smile. Our professional at-home whitening treatment is designed to tackle stubborn stains from everyday foods and drinks—delivered to your doorstep and performed in the comfort of your home.
What simple dietary swaps can help you restore your natural pearly whites?
Making a few small changes to your diet can protect your smile from further discolouration:
- Switch black tea for green or white tea – they contain fewer staining tannins.
- Rinse with water after eating dark-coloured foods – this reduces the time pigments stay on your teeth.
- Opt for crunchy fruit and veg like apples, celery, or carrots – they act as natural “toothbrushes”.
But dietary changes alone can only go so far. Aspire White’s Nottingham at-home laser whitening treatment complements these habits, removing existing stains so you can enjoy the benefits of your healthy swaps even faster.

Which foods actively brighten your smile while you enjoy them?
Some foods don’t just avoid staining—they actively help your teeth look cleaner:
- Strawberries – they contain malic acid, a natural enamel-brightener.
- Cheese – rich in calcium, it strengthens enamel and balances mouth acidity.
- Broccoli – its iron content creates a protective barrier on teeth.
Including these in your meals is a great habit, but for a fundamental transformation, pairing them with Aspire White’s Nottingham whitening technology ensures results you can see in days, not months.
What does scientific research say about diet-induced teeth staining—and where does Aspire White come in?
Research confirms that chromogens (pigment-producing molecules), tannins, and acids in food and drink are the leading causes of diet-related tooth discolouration. Over time, these compounds bind to the enamel surface, and regular brushing isn’t enough to remove them.
We combine advanced whitening science with the comfort of your own home. Our professional in-home laser whitening treatment breaks down stains at a molecular level, brightening your smile while protecting your enamel. You’ll get noticeable results without the hassle of long dental appointments.
When choosing between whitening toothpaste and dietary changes, what should tip the scale?
Whitening toothpaste can help maintain tooth brightness, but it typically works only on surface-level stains. Dietary changes can prevent new stains but won’t significantly lift existing discolouration. See How Shine Bright: The Truth About Laser Teeth Whitening
If you want a noticeable difference, the real game-changer is combining good habits with professional-grade whitening. Aspire White’s at-home laser whitening system delivers a more profound, longer-lasting transformation—without disrupting your daily routine.
What “whitening plate” meal ideas can you try tomorrow—curated by Aspire White Nottingham?
Here are three smile-friendly meal ideas to get you started:
Breakfast – Greek yoghurt with strawberries and a sprinkle of almonds.
Lunch – Grilled chicken salad with crunchy carrots, celery, and apple slices.
Dinner – Steamed salmon with broccoli and cauliflower, followed by a cube of cheese for dessert.
These meals not only taste great but also support your enamel health. Paired with Aspire White’s Nottingham at-home whitening treatment, you’ll be giving your smile the perfect inside-and-out care it deserves.